Fun & engaging podcast using NotebookLM
TL;DR! Listen to this amazing and fun podcast discussing below mentioned research papers!
Transforming healthcare with LLMs
This section contains LLMs applications in healthcare and bioinformatics. Researchers are leveraging these models to enhance disease detection, interpret complex medical data, and democratize bioinformatics analysis.
Enhancing Alzheimer's Detection with ADAM-1
Understanding and detecting Alzheimer's disease has been a persistent challenge. The ADAM-1: AI and Bioinformatics for Alzheimer's Detection and Microbiome-Clinical Data Integrations introduces a multi-agent LLM framework that integrates microbiome profiles, clinical datasets, and external knowledge bases. By synthesizing insights through retrieval-augmented generation, ADAM-1 improves research and diagnostic applications. Remarkably, it achieved mean F1 scores comparable to XGBoost but with significantly reduced variance, highlighting its robustness, especially with small laboratory datasets.
Interpretable Mental Health Diagnostics
Mental health diagnostics often grapple with complexity and the risk of errors. Large Language Models for Interpretable Mental Health Diagnosis proposes a clinical decision support system using LLMs to translate diagnostic manuals into logic programs. The implementation involves fine-tuning an LLM to understand and convert diagnostic criteria into constraint logic programming (CLP) rules. These logic programs are then executed by a CLP engine to simulate diagnostic reasoning. The system allows experts to inspect and modify the generated logic to ensure alignment with official diagnostic standards, enhancing interpretability. Validation is performed by comparing the system's outputs with established diagnoses, emphasizing the necessity of expert review to maintain fidelity to the manuals.
Advancing Radiology Report Generation with RadAlign

RadAlign: Advancing Radiology Report Generation with Vision-Language Concept Alignment presents a model that improves automated radiology report generation by aligning visual features with medical concepts. The implementation involves a vision-language model (VLM) that extracts visual features from radiological images and maps them to predefined medical concepts using a disease classification module achieving an AUC of 0.885. These concepts guide a LLMs equipped with retrieval-augmented generation to produce comprehensive reports. The system incorporates a concept alignment mechanism to ensure consistency between the visual input and textual output and employs error mitigation strategies to reduce inaccuracies, resulting in a GREEN score of 0.678 for report quality.
Democratizing Bioinformatics with BioAgents
Bioinformatics workflows are inherently complex, requiring interdisciplinary expertise. BioAgents: Democratizing Bioinformatics Analysis with Multi-Agent Systems introduces a multi-agent system utilizing small language models tailored for bioinformatics tasks. Enhanced with retrieval-augmented generation, this system allows for personalized, local use with proprietary data. The performance was comparable to human experts on genomics tasks, paving the way for more accessible bioinformatics analysis.
Stay up-to-date with AI
The Rundown is the most trusted AI newsletter in the world, with 1,000,000+ readers and exclusive interviews with AI leaders like Mark Zuckerberg, Demis Hassibis, Mustafa Suleyman, and more.
Their expert research team spends all day learning what’s new in AI and talking with industry experts, then distills the most important developments into one free email every morning.
Plus, complete the quiz after signing up and they’ll recommend the best AI tools, guides, and courses – tailored to your needs.
Code Generation
This section is for us! Let’s see how LLMs makes our work easy or in other words snatches our job! 😀
Automating Cloud Operations with MOYA

Managing cloud infrastructure can be complex and labor-intensive. Engineering LLM Powered Multi-agent Framework for Autonomous CloudOps presents MOYA, a multi-agent framework integrating various systems using generative AI. By addressing challenges like diverse data sources and complex task automation, MOYA enhances the management and optimization of cloud infrastructure. Practitioners observed improved accuracy and responsiveness across complex workflows.
Self-Reflective Code Generation with CodeCoR

CodeCoR: An LLM-Based Self-Reflective Multi-Agent Framework for Code Generation introduces a multi-agent approach where agents specialize in task prompts, code generation, test case creation, and repair advice. By producing multiple outputs and refining failing code based on testing outcomes, CodeCoR ensures robust final code delivery. It significantly outperformed baselines with an average Pass@1 score of 77.8%.
Hierarchical Code Summarization in Business Applications
Hierarchical Repository-Level Code Summarization for Business Applications Using Local LLMs presents a two-step summarization approach implemented with local LLMs to respect confidentiality. Initially, code is parsed into small units like functions and classes, which are summarized using LLMs with prompts tailored to capture technical details and business context. In the second step, these summaries are aggregated hierarchically to create summaries for larger structures such as files and modules, utilizing custom prompts that relate these components to overall business logic. The implementation ensures that the summarization captures both the technical and domain-specific aspects, which was validated in a telecommunications business support system, enhancing code comprehension and maintenance.
Enhancing GitHub Issue Resolution with SWE-Fixer
SWE-Fixer: Training Open-Source LLMs for Effective and Efficient GitHub Issue Resolution presents a framework with code retrieval and editing modules. Trained on an extensive dataset of 110K GitHub issues, SWE-Fixer achieved state-of-the-art performance among open-source models, facilitating effective issue resolution.
Advancements in Program Repair and Debugging
Several research papers have focused on automated program repair and debugging:
I Can Find You in Seconds! leverages LLMs for code authorship attribution, aiding in software forensics and plagiarism detection.
Evaluating Agent-based Program Repair at Google assesses the applicability of agent-based approaches for automated bug fixing in an enterprise environment, achieving plausible patch creation for 73% of evaluated bugs.
How is Google using AI for internal code migrations? shares insights into Google's application of LLMs for enterprise-level code migration, demonstrating significantly reduced migration times.
AIOpsLab: A Holistic Framework to Evaluate AI Agents for Enabling Autonomous Clouds introduces a framework that evaluates AI agents in cloud environments, contributing to the development of self-healing systems.
Debugging Without Error Messages explores how different LLM prompting strategies can enhance programming error explanations, aiding educators and novice programmers.
AI agents in autonomous systems
AI agents and multi-agent systems is opening new avenues for automation, collaboration, and efficiency across various domains. This section is dedicated to such papers!
Dynamic Workflow Generation with Flow
Flow: A Modular Approach to Automated Agentic Workflow Generation introduces workflows as activity-on-vertex graphs to emphasize modularity. By refining workflows through dynamic task allocations based on historical performance, the framework enhances efficiency and error tolerance, showing substantial improvements in handling practical tasks.
Integrating AI Agents with Web3 Applications through Eliza

Eliza: A Web3 Friendly AI Agent Operating System addresses the integration gap between AI agents and Web3 applications. Developed fully in TypeScript, Eliza allows users to deploy Web3 applications effortlessly. It facilitates interaction with blockchain data and smart contracts while ensuring stable performance through optimized runtime components.
Automating Systematic Reviews with LatteReview
LatteReview: A Multi-Agent Framework for Systematic Review Automation Using LLMs leverages LLMs and multi-agent systems to automate tasks like title screening and data extraction. By incorporating features like retrieval-augmented generation and asynchronous programming, LatteReview handles large datasets efficiently, integrating with both cloud-based and local models.
Context-Aware Storytelling with MDSF (Uncovers aha moment from data!)

Data storytelling is becoming increasingly important. MDSF: Context-Aware Multi-Dimensional Data Storytelling Framework Based on Large Language Model introduces a framework that uses LLMs for automated insight generation and storytelling. With advanced preprocessing, analysis algorithms, and an agent-based storytelling continuation control, MDSF outperforms existing methods in insight ranking accuracy and narrative coherence.
Democratizing LLM Services with LLM-Net
LLM-Net: Democratizing LLMs-as-a-Service through Blockchain-based Expert Networks presents a decentralized blockchain framework creating a network of specialized LLM providers. By leveraging collective computational resources and incorporating reputation-based mechanisms, LLM-Net ensures high service quality and facilitates seamless AI advancement across multiple domains.
Domain adoption
Enhancing Labor Market Analytics
Enhancing Talent Employment Insights Through Feature Extraction with LLM Finetuning utilizes semantic chunking, retrieval-augmented generation, and fine-tuning of DistilBERT models to process over one million job postings. The fine-tuned models significantly improved the identification of complex job features like remote work availability and remuneration structures.
Automated Crypto Portfolio Management
Cryptocurrency investments requires multi-modal data and intricate reasoning. LLM-Powered Multi-Agent System for Automated Crypto Portfolio Management employs specialized LLM agents that collaborate for tasks like data analysis and investment decision-making. Fine-tuned with historical data and enhanced with unique collaboration mechanisms, the framework outperformed single-agent models in classification, asset pricing, portfolio management, and explainability.
Optimizing Home Energy Management
Simplifying home energy management systems (HEMS) for non-technical users is important. Large Language Model Interface for Home Energy Management Systems presents an LLM-based interface that transforms poorly formatted user input into well-structured parameters. Using the Reason and Act method and few-shot prompting, the system achieved an average parameter retrieval accuracy of 88%, enhancing user interaction with power systems.
Power Grid Optimization with SafePowerGraph-LLM

Modern power grids face increasing complexity. SafePowerGraph-LLM: Novel Power Grid Graph Embedding and Optimization with Large Language Models introduces a framework that leverages LLMs combined with graph and tabular representations to solve Optimal Power Flow problems. Utilizing in-context learning and fine-tuning protocols, the framework reliably handled realistic grid components and constraints, demonstrating the impact of LLM architecture on performance.
Improving Time Series Forecasting with Pre-trained LLMs
Using Pre-trained LLMs for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting leverages the capabilities of pre-trained LLMs by mapping multivariate inputs into the LLM's token embedding space. Utilizing a novel multivariate patching strategy, the approach embeds features into decoder-only pre-trained transformers. The results are competitive with state-of-the-art forecasting models, showcasing the potential of LLMs in complex data analysis tasks.
Innovative FPGA Architecture for Efficient Computing
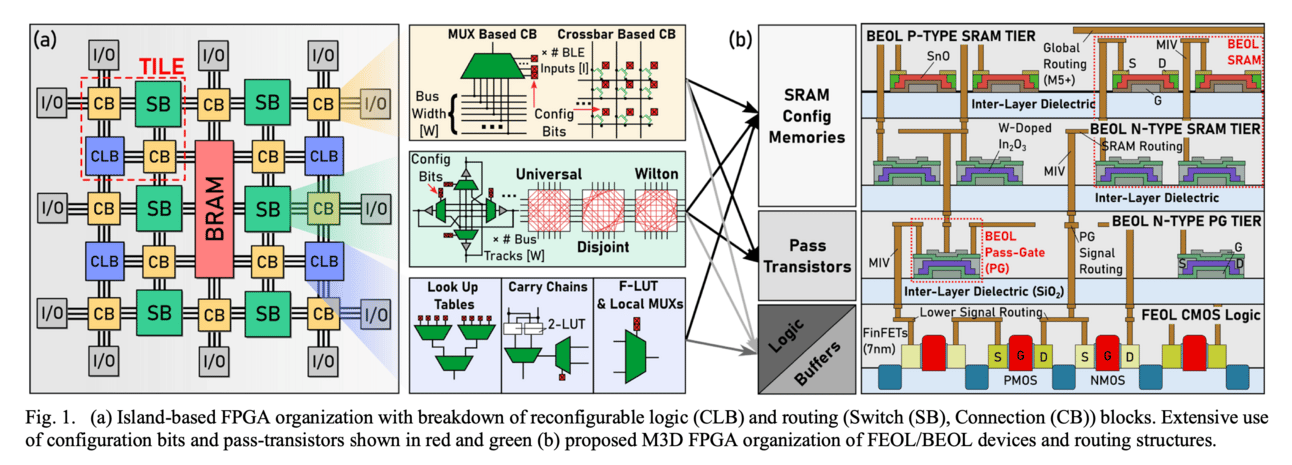
Monolithic 3D FPGAs Utilizing Back-End-of-Line Configuration Memories introduces a novel FPGA architecture that significantly improves area, latency, and power efficiency. By using back-end-of-line (BEOL) transistors for configuration memory and pass gates, and integrating n-type and p-type amorphous oxide semiconductors (AOS) under development, the researchers developed physics-based models interfaced with Verilog-to-Routing tools. Demonstrated at 7 nm technology, the proposed M3D FPGA design reduces the area-time squared product by 3.4x and decreases critical path latency by 27%. This advancement has broad implications for industries relying on efficient computing, including the deployment of LLMs.
Robotics/VLLMs application/improvement
Advancing 3D Scene Understanding with 3UR-LLM

3UR-LLM: An End-to-End Multimodal Large Language Model for 3D Scene Understanding addresses this by building the 3DS-160K dataset and introducing a model that processes 3D point cloud data. Utilizing a 3D compressor module, the model efficiently handles computation demands, outperforming previous state-of-the-art models by 7.1% on relevant benchmarks.
VLMs as Operator Agents in Space
Visual Language Models as Operator Agents in the Space Domain explores the application of Vision-Language Models in autonomous control and decision-making for space missions. In both software simulations and hardware contexts, VLMs effectively processed visual inputs to perform orbital maneuvers and inspect space objects. These models compete with or outperform traditional methods, showing promise for future space exploration.
Compositional Text-to-Video Generation with BlobGEN-Vid
Generating videos that accurately reflect complex text prompts is a very challenging task. BlobGEN-Vid: Compositional Text-to-Video Generation with Blob Video Representations introduces a model that uses blob-grounded video diffusion to control object motions and appearances. With enhanced regional consistency and semantic control, BlobGEN-Vid demonstrates superior zero-shot video generation capabilities, surpassing proprietary generators in compositional accuracy.
Affective Tactile Interaction Driven by LLMs

Touched by ChatGPT: Using an LLM to Drive Affective Tactile Interaction leverages LLMs to generate tactile signals that convey emotions. Using a wearable sleeve equipped with vibration motors, unique patterns associated with specific emotions were generated. Participants accurately recognized intended emotions, demonstrating the effectiveness of LLMs in communicating emotion via tactile signals.


