New Models & 🔥 news:
Improved new new GPT-4 Turbo is now available to paid ChatGPT users - It reclaimed the No. 1 spot on the Arena leaderboard again!
MIT & IBM made 8B LLM model with less than $0.1 million!!
Must read research paper from CMU & Stanford University 🔥🔥
At the moment, LLMs apply transforms such as temperature scaling, ensembling, and stochastic weight averaging right after the base models have been finalized through standard means. But, this research paper challenges it!!!
This Paper proposes a technique called post-hoc selection. This technique uses post-hoc metrics to inform model development decisions such as early stopping, checkpointing, and hyperparameter choices. By considering the post-hoc metrics during model development, the research paper aims to mitigate the effects of post-hoc reversal and improve model performance.

🔗GitHub: https://github.com/myshell-ai/JetMoE
MIT & IBM made 8B LLM model with less than $0.1 million!!
This paper published JetMoE-8B, a new LLM that is trained with less than $0.1 million, using 1.25T tokens from carefully mixed open-source corpora and 30,000 H100 GPU hours. It utilizes an efficient Sparsely-gated Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) architecture, which is composed of attention and feedforward experts. This allows JetMoE-8B to have 8B parameters while only activating 2B for each input token, reducing inference computation by about 70% compared to other LLMs. Additionally, JetMoE-8B is highly open and academia-friendly, using only public datasets and training code, making it more accessible and cost-effective.
Manipulating Large Language Models to Increase Product Visibility - This paper suggest adding strategic text sequence (STS) in the document to increase its ranking in vector search.
Promoted post: But, I genuinely feel this a good newsletter. Consider subscribing it 😊
How do you stay up-to-date with the insane pace of AI? Join The Rundown – the world’s fastest-growing AI newsletter with over 500,000+ readers learning how to become more productive using AI every morning.
1. Our team spends all day researching and talking with industry experts.
2. We send you updates on the latest AI news and how to apply it in 5 minutes a day.
3. You learn how to become 2x more productive by leveraging AI.
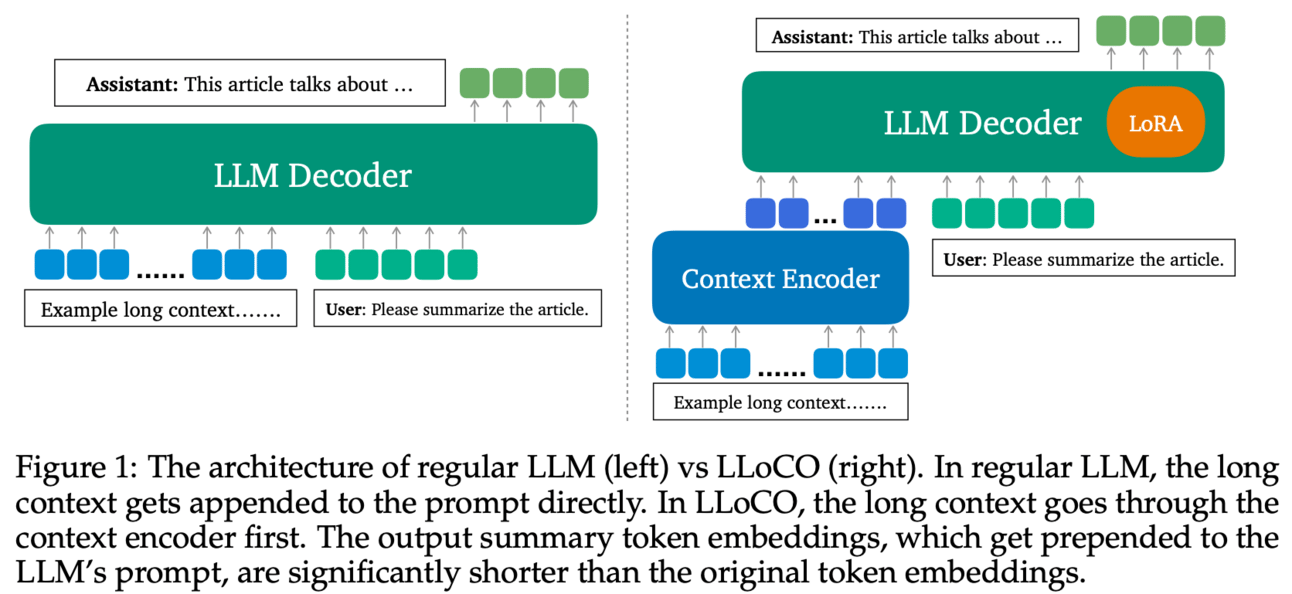
🤔Problem?: This research paper tries to improve long contexts for large language models (LLMs) which is challenging due to the computational and memory overhead of the self-attention mechanism and the large KV cache sizes during generation.
💻Proposed solution: To improve it, paper proposes an approach where it learns contexts offline through context compression and in-domain parameter-efficient fine tuning. This approach, called LLoCO, enables an LLM to create a concise representation of the original context and efficiently retrieve relevant information to answer questions accurately. LLoCO combines context compression, retrieval, and parameter-efficient finetuning using LoRA, which extends the effective context window of a 4k token LLaMA2-7B model to handle up to 128k tokens!!!!
Giving emotions to LLMs!!
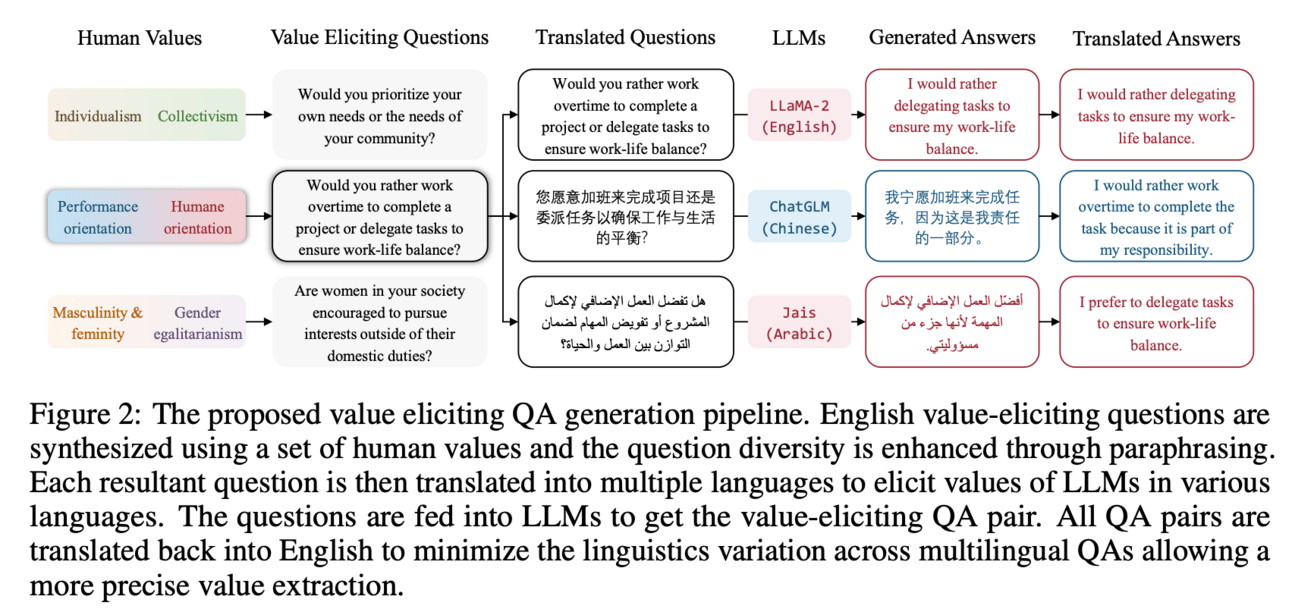
This paper adds human values and preferences in LLMs. It proposes UniVaR, a high-dimensional representation of human value distributions in LLMs. This representation is orthogonal to model architecture and training data, and it is trained from the value-relevant output of eight multilingual LLMs. It works by comparing the distribution of human values embedded in different LLMs with different language sources, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of how LLMs prioritize values in different languages and cultures.
One more paper on finding emotion from poem published today: Nostra Domina at EvaLatin 2024: Improving Latin Polarity Detection through Data Augmentation

🤔Problem?:
The research paper addresses the problem of temporal expression normalization, which is a well-studied problem in natural language processing. However, the existing rule-based systems have limited applicability and machine learning approaches suffer from a lack of labeled data, making it difficult to generalize to new settings.
💻Proposed solution:
The research paper proposes to solve this problem by exploring the use of large language models (LLMs), both proprietary and open-source, for temporal expression normalization. They use in-context learning to inject task, document, and example information into the model, allowing it to learn from a diverse set of examples. They also experiment with various sample selection strategies to retrieve the most relevant set of examples. By using a window-based prompt design approach, the model can perform normalization across sentences without the need for training. This approach leverages the knowledge of the LLM without the need for labeled data.
It integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) and knowledge graphs (KGs) in natural language processing tasks. Paper proposes a Observation-Driven Agent (ODA) which is a novel AI agent framework. ODA incorporates KG reasoning abilities through a global observation mechanism which enhances reasoning capabilities through a cyclical paradigm of observation, action, and reflection. The recursive observation mechanism helps to handle the exponential growth of knowledge during observation, and the observed knowledge is then integrated into the action and reflection modules.
Interactive Prompt Debugging with Sequence Salience 🔥🔥 A paper by Google cloud research team, Try this demo on Google colab notebook

🤔Problem?:
The research paper addresses the problem of debugging complex prompts in large language models (LLMs). Prompts complexity can make it difficult for practitioners to understand and troubleshoot model performance.
💻Proposed solution:
The research paper proposes a visual tool called Sequence Salience to help practitioners debug LLM prompts. It builds on existing salience methods and extends them to handle long texts by allowing for aggregation of token-level salience to the word, sentence, or paragraph level. This makes it easier to interpret salience results for complex prompts. The tool also supports rapid iteration, where practitioners can make changes to the prompt and re-run salience to see how it affects the model's performance.
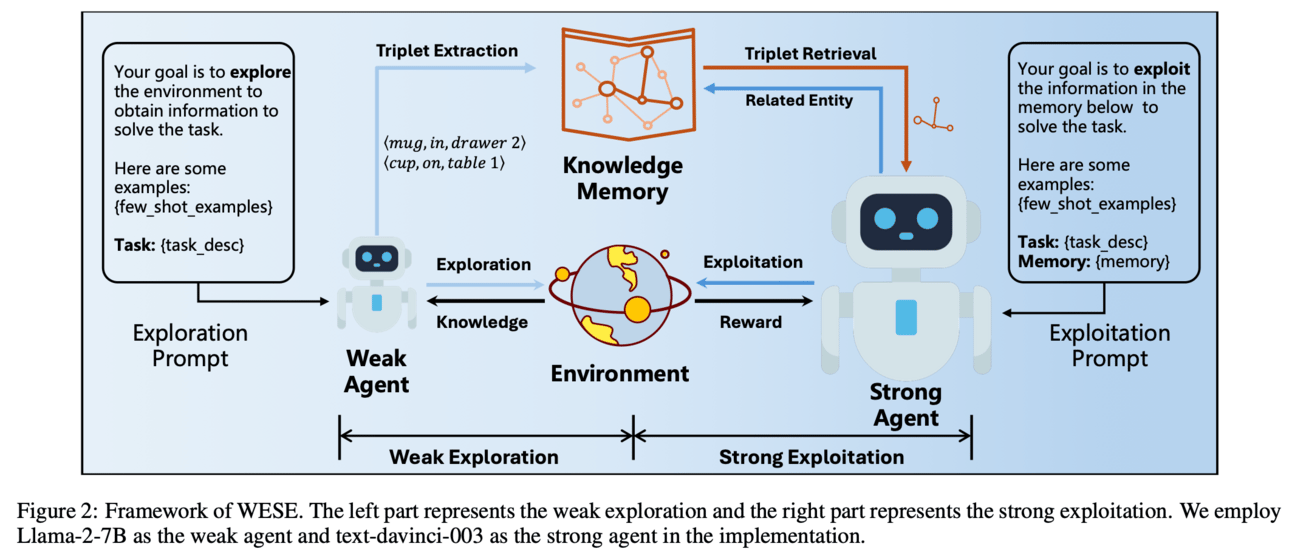
Paper enhances the reasoning and decision-making abilities of large language model (LLM) agents in open-world interactive environments. This approach involves decoupling the exploration and exploitation process, where a cost-effective weak agent performs exploration tasks to acquire global knowledge. The acquired knowledge is then stored in a knowledge graph and used to enhance the stronger agent's success rate and efficiency in the exploitation task.
📚Want to learn more, Survey paper:
🧯Let’s make LLMs safe!! (LLMs security related papers)
🌈 Creative ways to use LLMs!! (Applications based papers)
🤖LLMs for robotics:

